Internet node
Forward Enterprise allows users to define a synthetic device called an Internet node that represents the Internet or third-party public network infrastructure.
The Internet node enables users to trace paths between different sites connected via the public internet or a third-party IP infrastructure, providing visibility for end-to-end path analysis.
The Internet node can be connected to one or more sites and includes the public subnet(s) of the connected site (s). Public subnets not associated with any site will be located at this node on a port called self, used by the Forward platform to aid in path modeling.
In the example below, the user can trace paths across sites through the Internet node. For example, a query could be _ from 88.123.8.15 to 77.123.8.25_.
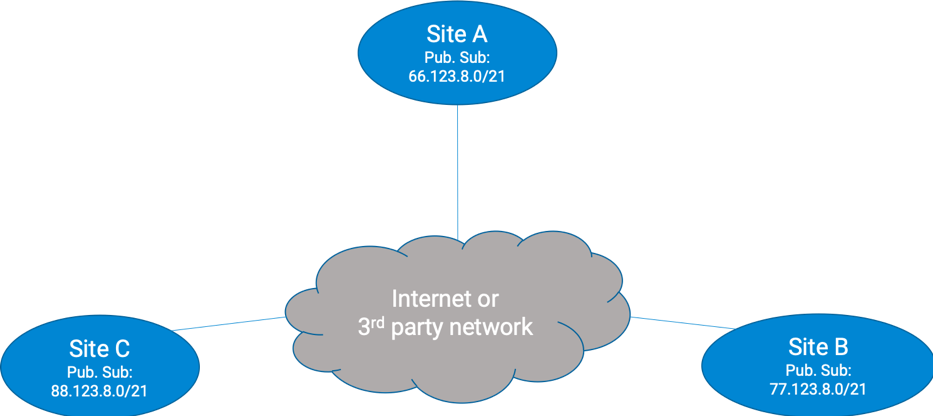
Forward creates an Internet node per Network. Users can configure it but cannot change its name, delete it, or create a new one.
The Internet node can be configured via the Forward Enterprise GUI or REST APIs.
Configure the Internet node via the Forward Enterprise GUI
To configure the Internet node via the Forward Enterprise GUI, navigate to the Sources page, select the Synthetic Devices category, and click the edit icon on the right side of the Internet node.
To configure one or more Connections, select + Add connections and choose one of the following options:
- Batch-add NQE-based connections: This option allows you to add multiple connections at once based on an NQE query.
- Add a connection manually: This option allows you to add connections individually, specifying detailed information for each connection.
Batch-add NQE-based connections
To add connections based on an NQE query, select Batch-add NQE based connections and select an NQE query from NQE query dropdown.
To create a new query, click + Add new query from template. This will navigate to the NQE Library, where you can edit the newly created query in the NQE editor and commit it when finished. Return to the Synthetic Devices page to add the NQE query.
-
When an NQE query attached to an Internet node is modified, the system recomputes and saves the dynamic connections. These changes take effect in the next processed snapshot.
-
Upon processing a new snapshot, the system recalculates the results for the NQE query linked to the existing Internet node and updates the dynamic connections. These updates apply to the next processed snapshot.
Add a connection manually
To manually add a connection to an Internet node, select Add a connection manually and provide the following for each connection:
- Uplink interface: Device and interface of the site to which the Internet node connects. This can be an L2 or L3 interface.
- VLAN (optional): VLAN on the link that connects the Internet node to the site.
- Gateway interface (optional): The last L3 interface that routes traffic to this synthetic device. Defaults to the Uplink interface (with VLAN) if not specified. Note: This does not need to reside on the same device as the Uplink interface.
- Connection name (optional): a custom name for the interface created on the Internet node for this connection. If not provided, one will be created automatically from the gateway interface name.
- Site (optional): the name of the site in which this connection's gateway device resides. A site is a collection of devices that redistribute routes learned from an internet (or intranet) to each other. Grouping gateway devices into a single device enables more accurate subnet auto-discovery.
- Subnet auto-discovery: subnets attached to the connection can be provided manually or discovered automatically by
examining either the gateway device's routing table or its advertised BGP routes.
- Off: no site subnet discovery is performed. Subnets must be supplied in the Subnets list.
- From interface addresses: the gateway interface's public addresses are used as site subnets.
- From IP routes: site subnets are discovered by examining the gateway device's routing table. Any public subnet forwarded out a port other than the gateway is considered a site subnet.
- From BGP routes: site subnets are discovered by examining the gateway device's BGP advertised routes (post-policy Adj-RIB-Out). Any subnet advertised to a BGP neighbor is considered a site subnet. This can be restricted to routes advertised to a specific set of BGP neighbors using the optional Peer IPs list. In the example below, all public subnets advertised to BGP neighbor 1.1.1.1 will be site subnets.
- Advertises the default route: whether this customer edge device advertises the default route.
- Backdoor ports (optional): This feature prevents the synthetic device from learning routes forwarded through specific ports. With From IP routes Forward treats any route forwarded out a non-gateway port as advertised. If a gateway has a backdoor or tunnel link to another site, it may appear to advertise that site’s prefixes, even though the connection is not part of the internet node. To avoid this, mark the tunnel as a backdoor port so Forward ignores routes forwarded through it when inferring advertised routes.
The Internet node location will be automatically inferred based on its connections.
Changes to the Internet node will be applied to the next collected snapshot.
BGP advertisements to eBGP peers will be collected from gateway devices connected to an Internet node that use BGP_ROUTES subnet auto-discovery. For instructions on manually configuring or disabling collection of BGP advertisements, see the BGP Advertisement Configuration page.
Edit and review connections
The newly added connections are displayed in a table with the following options: Manage NQE-based connections
- Change the query: Opens the Edit NQE-based connections drawer to change the currently selected query.
- Delete all Deletes all NQE-based connections.
+ Add Connections
- Batch-add NQE-based connections: Select this option to add an NQE-based query to batch-add connections. Only one NQE query can be selected at a time. To include additional connections, edit the existing NQE query.
- Add a connection manually: Select this option to add a connection manually.
Editing manually added connections
Select the edit icon at the end of each row to edit a manually added connection.
Deleting manually added connections
Select the delete icon at the end of each row to delete a manually added connection.
Select Save when ready.
Managing Internet nodes
You can edit an Internet node by clicking on the Edit icon on the right side of the Synthetic Devices page.
Newly added L2 VPNs, or any change to existing L2 VPNs, will be shown in the following collected snapshot.
Configure an Internet node via the Forward Enterprise REST APIs
The Internet node can be configured via the Forward Enterprise REST APIs via the endpoint PUT:
/api/snapshots/{snapshotId}/internetnode.
Subnets can be provided manually in the connection's subnets list, as in the example below:
{
"name": "internet",
"connections": [
{
"uplinkPort": {
"device": "atl-internet",
"port": "ge-0/0/0"
},
"subnets": ["123.223.47.0/24"]
}
]
}
The following example shows how to discover the subnets automatically from BGP routes and how to restrict to routes advertised to a given BGP neighbor:
{
"name": "internet",
"connections": [
{
"uplinkPort": {
"device": "atl-internet",
"port": "ge-0/0/0"
},
"gatewayPort": {
"device": "atl-internet",
"port": "vlan100"
},
"name": "atl0/0",
"site": "atl",
"subnetAutoDiscovery": "BGP_ROUTES",
"peerIps": [
"1.1.1.1"
]
}
]
}
For more info on Internet node APIs, including endpoints to add/remove connections and remove an Internet node, please check the Synthetic Devices REST API docs.