Predefined Verification
Predefined Checks are built-in checks that allow users to easily verify common configuration and state constructs across the entire network.
The following are just a few examples:
- BGP Neighbor Adjacency: For each BGP neighbor, the adjacency should be established and at least one route received from that neighbor
- VLAN Consistency: VLANs should be consistently defined on interfaces on either side of each link in the network
- Duplex Consistency: Interfaces at both ends of each link should have the same duplex type configured
- MTU Consistency: Interfaces at both ends of each link should have the same MTU. Values are normalized to include only L3 fields and up
This section of the documentation describes the library of Predefined Verification Checks available out of the box with Forward. These Predefined Verification Checks are applicable to many network environments and provide an easy starting point to capture the platform's value against some common sources of network issues. The list of available checks in this library keeps on growing thanks to the constant feedback from our users.
Enabling the Predefined Checks
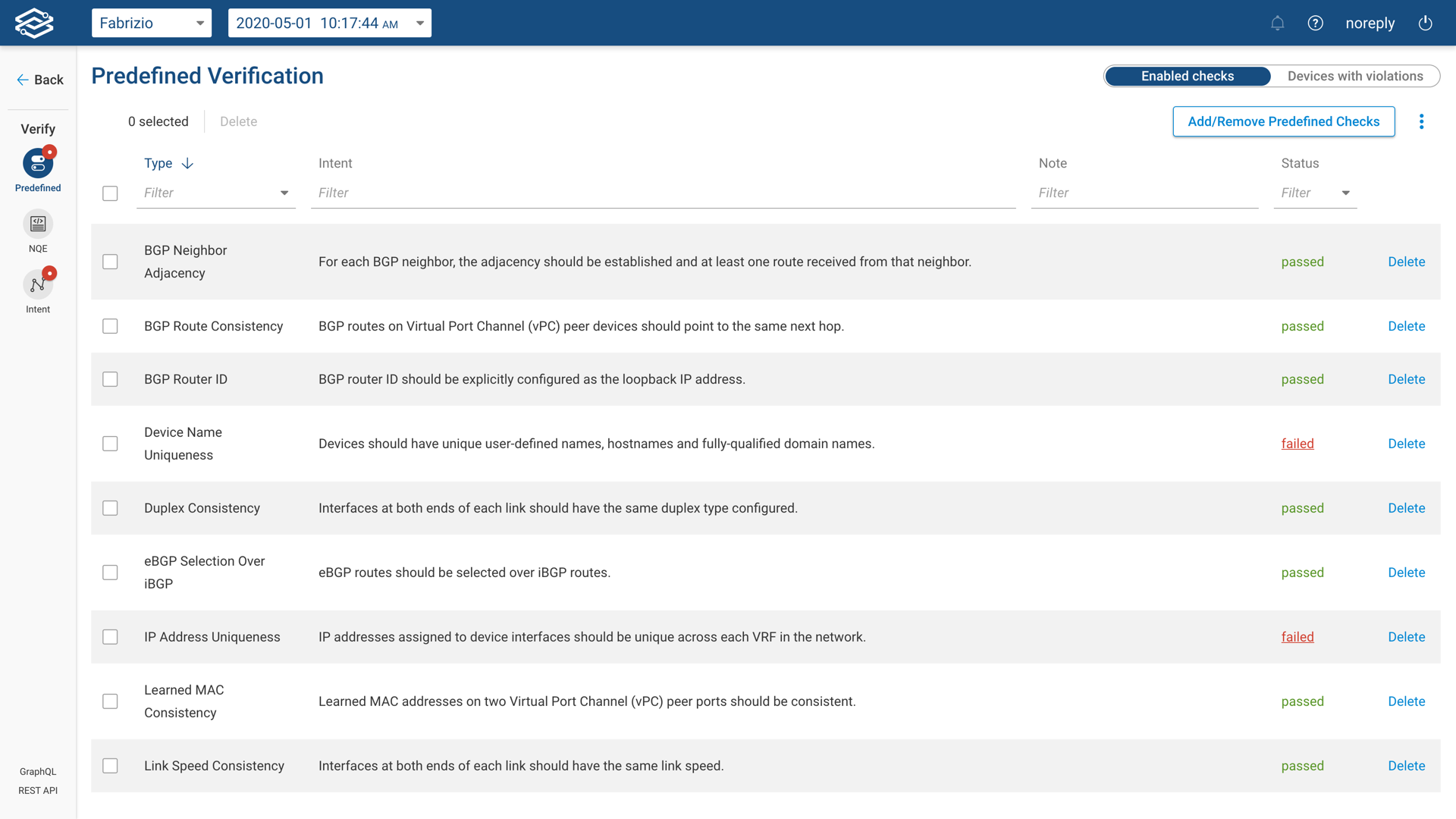
By going to the Verify page (shown above), the user can explore the checks that have already been enabled. A red icon on the tab's label indicates how many checks are currently failing.
To enable or disable each predefined check the user can click the link on the upper right corner of the table.
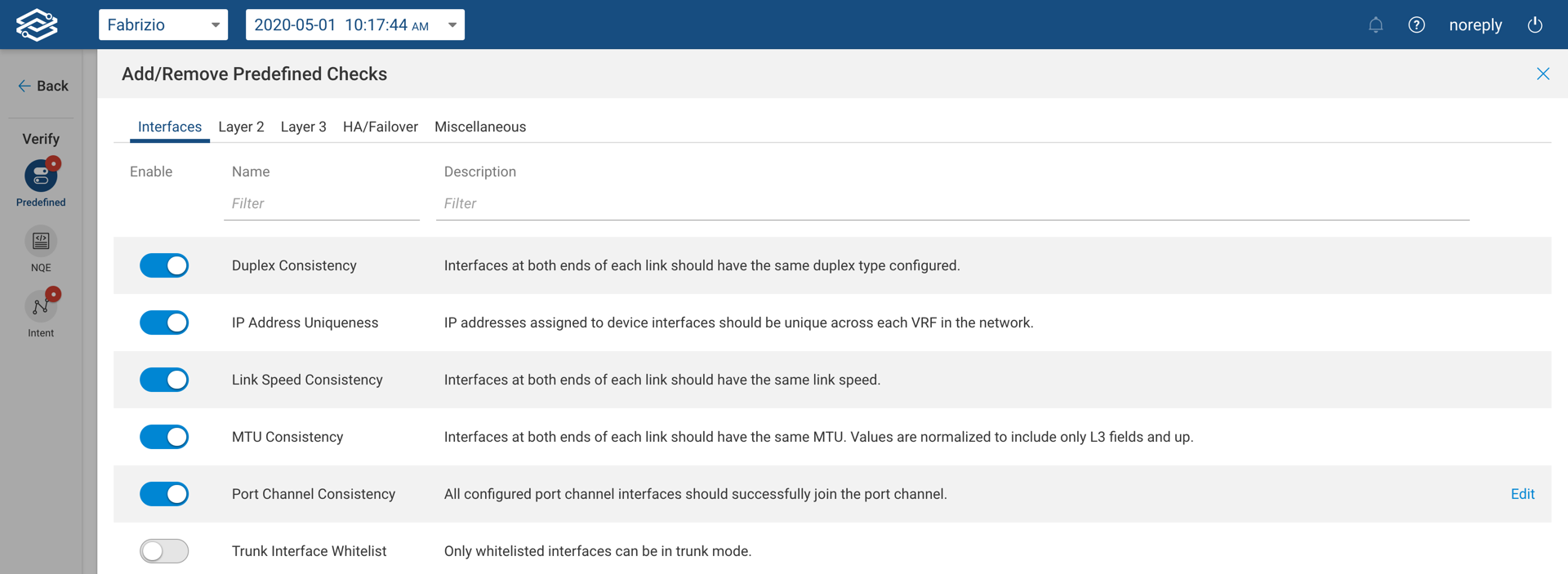
The Predefined Checks are grouped based on the networking area they cover. Enabling a predefined verification check is extremely easy and it's done by toggling the button to the left of each check. Once enabled each check will run immediately against the current snapshot.
Predefined Checks for Interfaces
- Duplex Consistency - Interfaces at both ends of each link should have the same duplex type configured.
- IP Address Uniqueness - IP addresses assigned to device interfaces should be unique across each VRF in the network.
- Link Speed Consistency - Interfaces at both ends of each link should have the same link speed.
- MTU Consistency - Interfaces at both ends of each link should have the same MTU. Values are normalized to include only L3 fields and up.
Some network platforms report the interface MTU size differently than configured. This happens when the line of MTU
configuration includes the Layer-2 header fields, but the show interface command (or equivalent) output includes only
Layer-3 header fields and up. To reduce confusion, the collected interface data is normalized and the MTU Consistency
predefined check only takes Layer-3 fields and up when comparing the interfaces.
- Port Channel Consistency - All configured port channel interfaces should successfully join the port channel.
- Trunk Interface Whitelist - Only whitelisted interfaces can be in trunk mode.
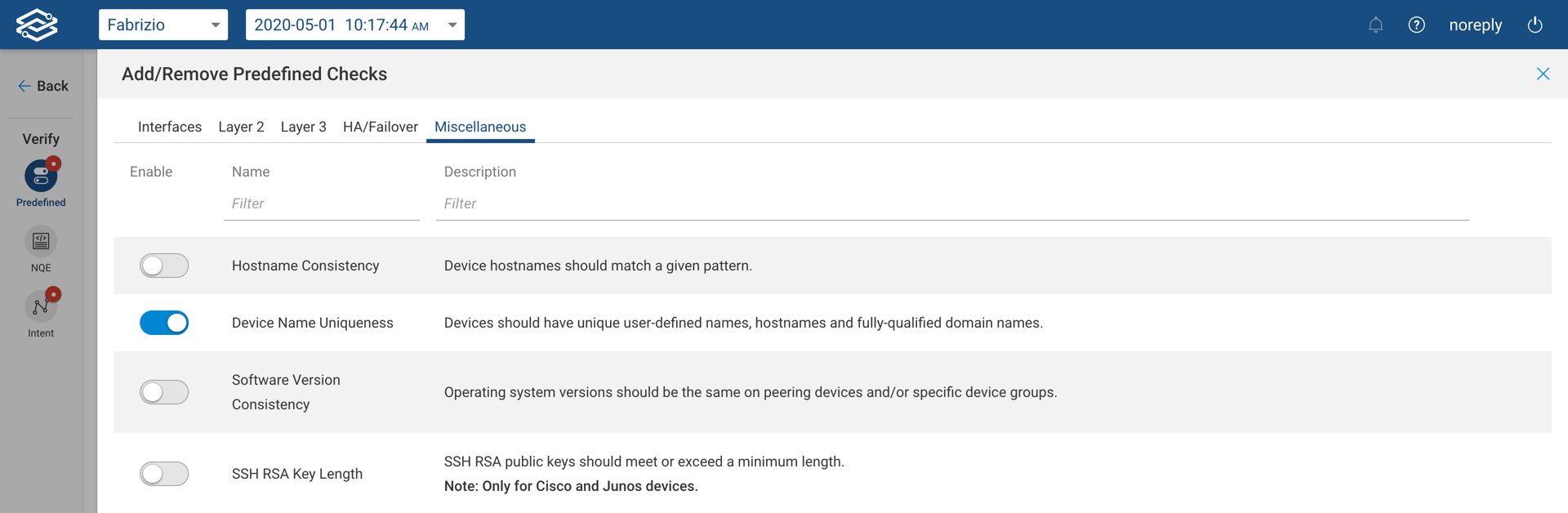
Predefined Checks for Layer 2
- VLAN Consistency - VLANs should be consistently defined on interfaces on either side of each link.
- VLAN Existence - Edge trunk interfaces must carry all specified VLANs.
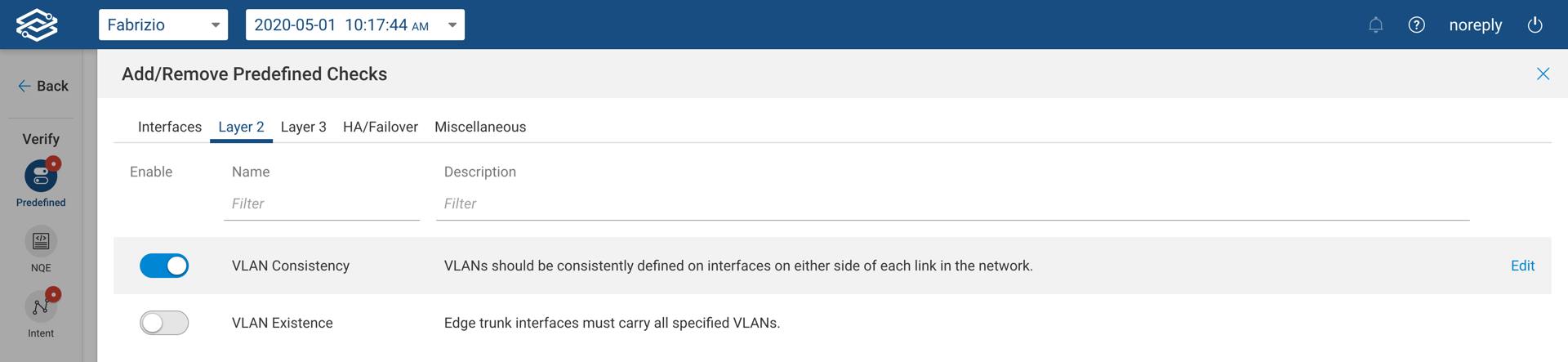
Predefined Checks for L3
- BGP Route Consistency - BGP routes on Virtual Port Channel (vPC) peer devices should point to the same next hop ( Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- BGP Neighbor Adjacency - For each BGP neighbor, the adjacency should be established and at least one route received from that neighbor (Cisco and Junos devices only).
- BGP Router ID - BGP router ID should be the loopback IP address (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- BGP Parameter Consistency for vPC Peers - BGP parameters should be the same on Virtual Port Channel (vPC) peer devices (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- BGP Community List - BGP advertised routes should be tagged with expected community value (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- eBGP selection over iBGP - eBGP routes should be selected over iBGP routes (Cisco and Junos devices only).
- Next Hop Reachability - Routes should have reachable next hops in the routing table.
- No Forwarding Loops - There should be no traffic forwarding loops in the network.
- Shortest Path - All traffic between device groups should take the shortest network path.
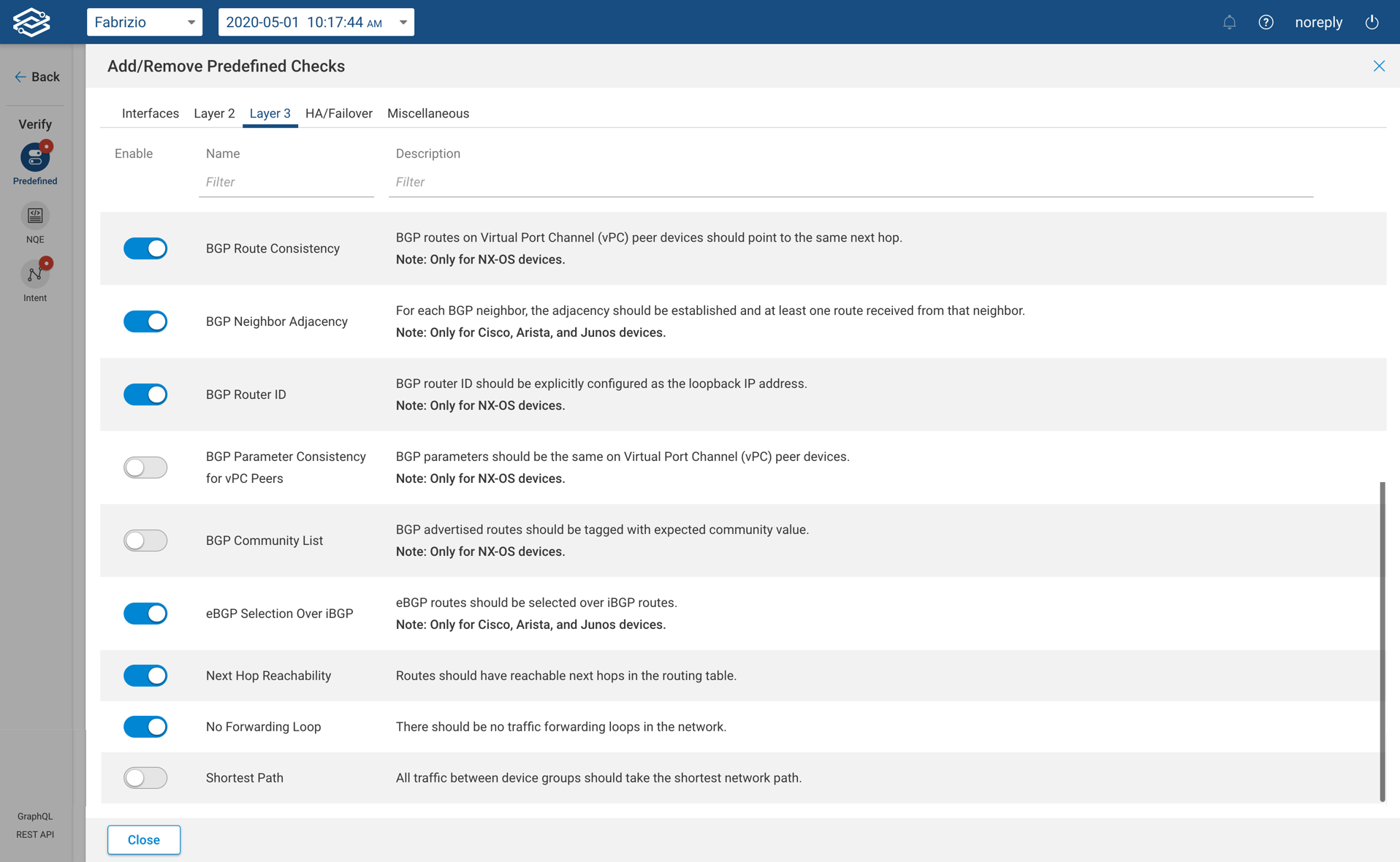
Predefined Checks for HA and Fail-over
- Learned MAC Consistency - Learned MAC addresses on two Virtual Port Channel (vPC) peer ports should be consistent (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- vPC Global Parameter Consistency - Virtual Port Channel (vPC) global parameters on two vPC peers should be consistent (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- vPC Interface Parameter Consistency - Virtual Port Channel (vPC) interface parameters on two vPC peers should be consistent (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- vPC MST Region Consistency - Virtual Port Channel (vPC) peers must have same MST region configuration (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- Dedicated vPC Keepalive Link - Virtual Port Channel (vPC) keepalive traffic should be on dedicated link (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- vPC Role Priority - Virtual Port Channel (vPC) role priority should be set, optionally to specified values (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- vPC STP Priority - Virtual Port Channel (vPC) peers must have non-default STP priorities configured (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
- Successful FHRP Peering - VRRP/HSRP peering should be successfully established (Cisco NX-OS devices only).
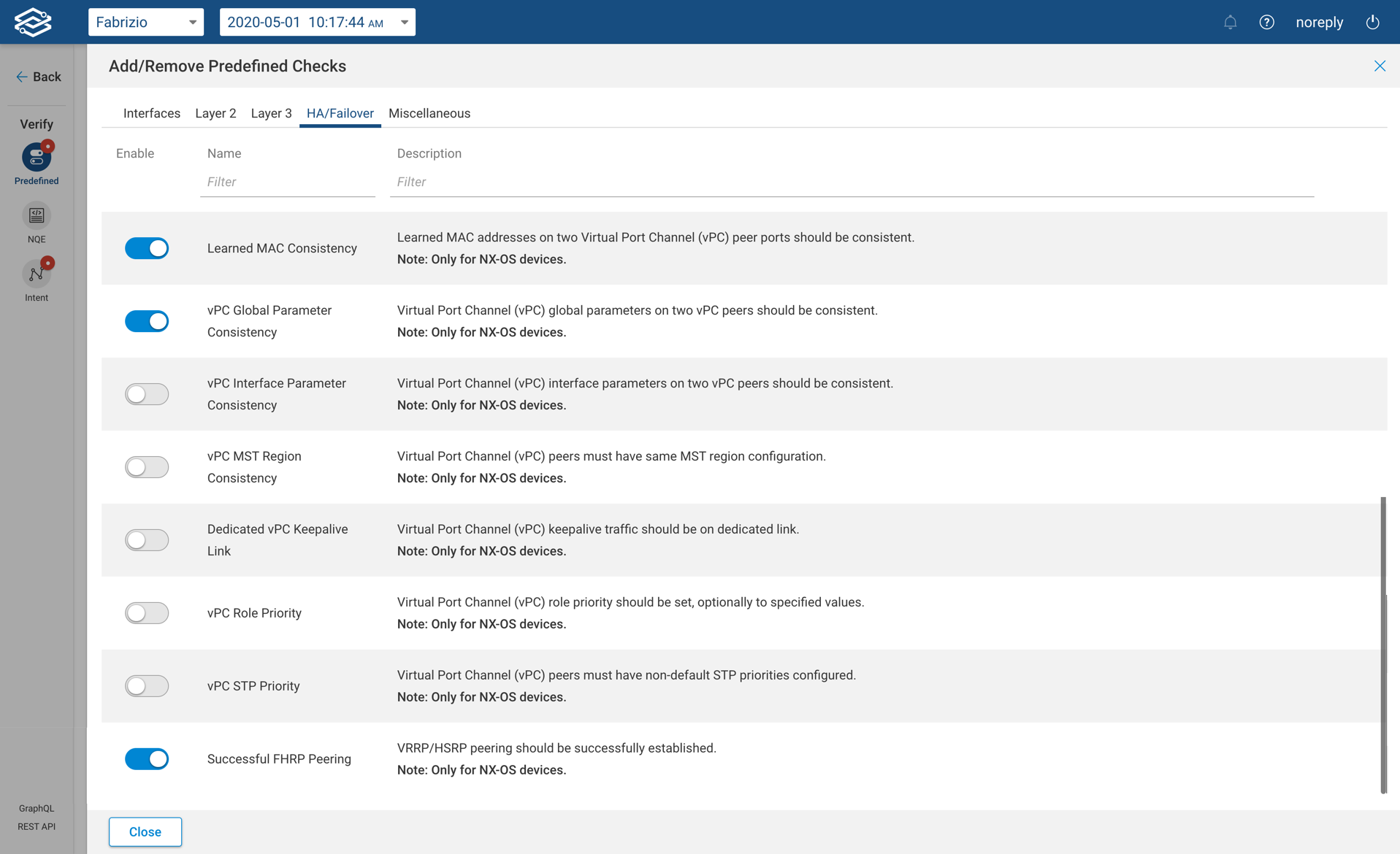
Other Predefined Checks
- Hostname Consistency - Device hostnames should match a given pattern.
- Device Name Uniqueness - Devices should have unique user-defined names, hostnames and fully-qualified domain names.
- Software Version Consistency - Operating system versions should be the same on peering devices and/or specific device groups.
- SSH RSA Key Length - SSH RSA public keys should meet or exceed a minimum length (only for Cisco and Junos devices) .
- No Forwarding Loop - There should be no Layer 3 forwarding loops in the network.
- Shortest Path - All traffic between device groups should take the shortest network path.
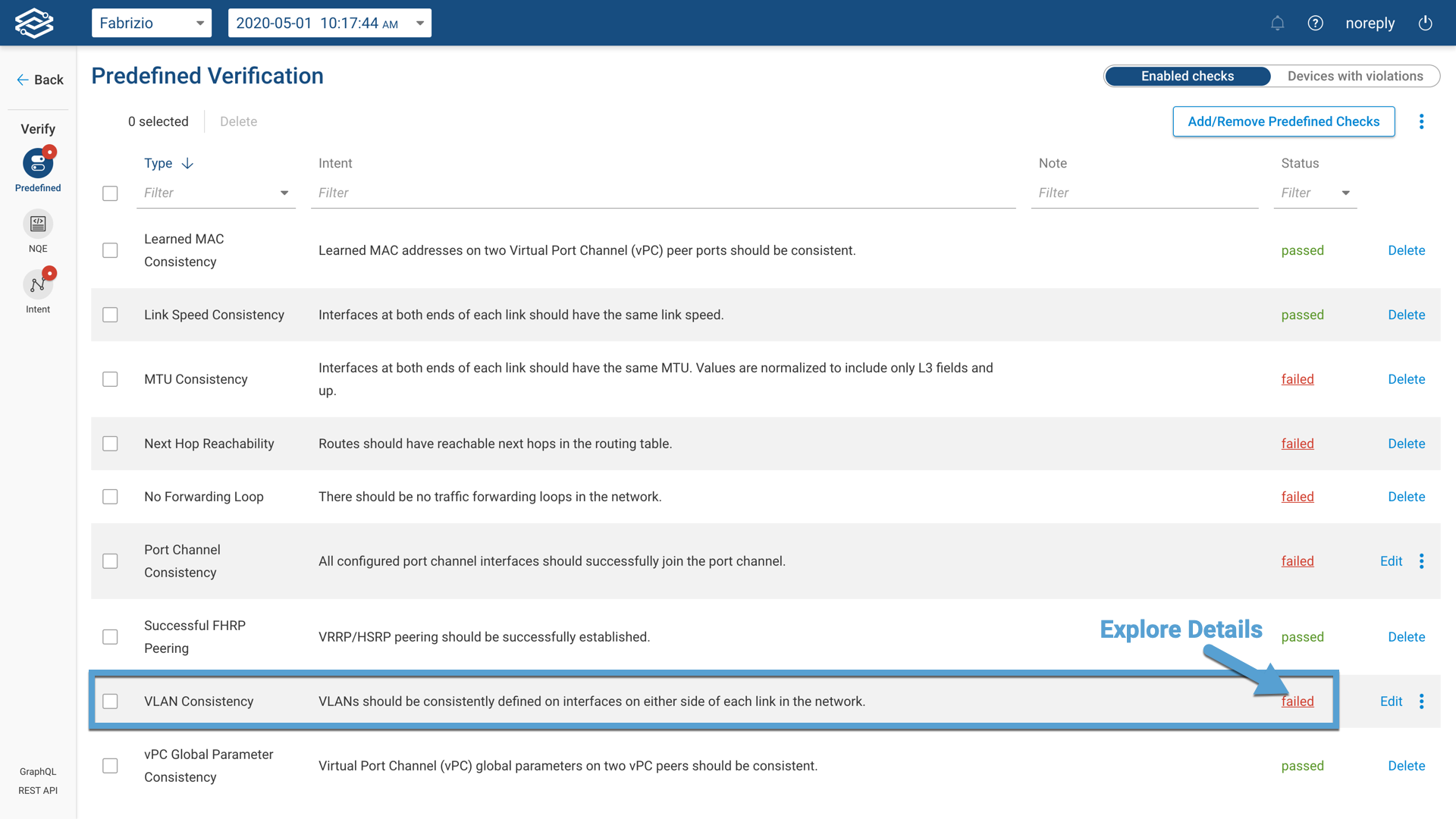
Exploring the Predefined Checks Failures
By clicking on the "Predefined Checks" tab on the Verify page, the user can explore the status of each enabled on the Status column. For each failing check, the user can click on the "failed" red link on the status column to explore where in the network and how the check is failing.
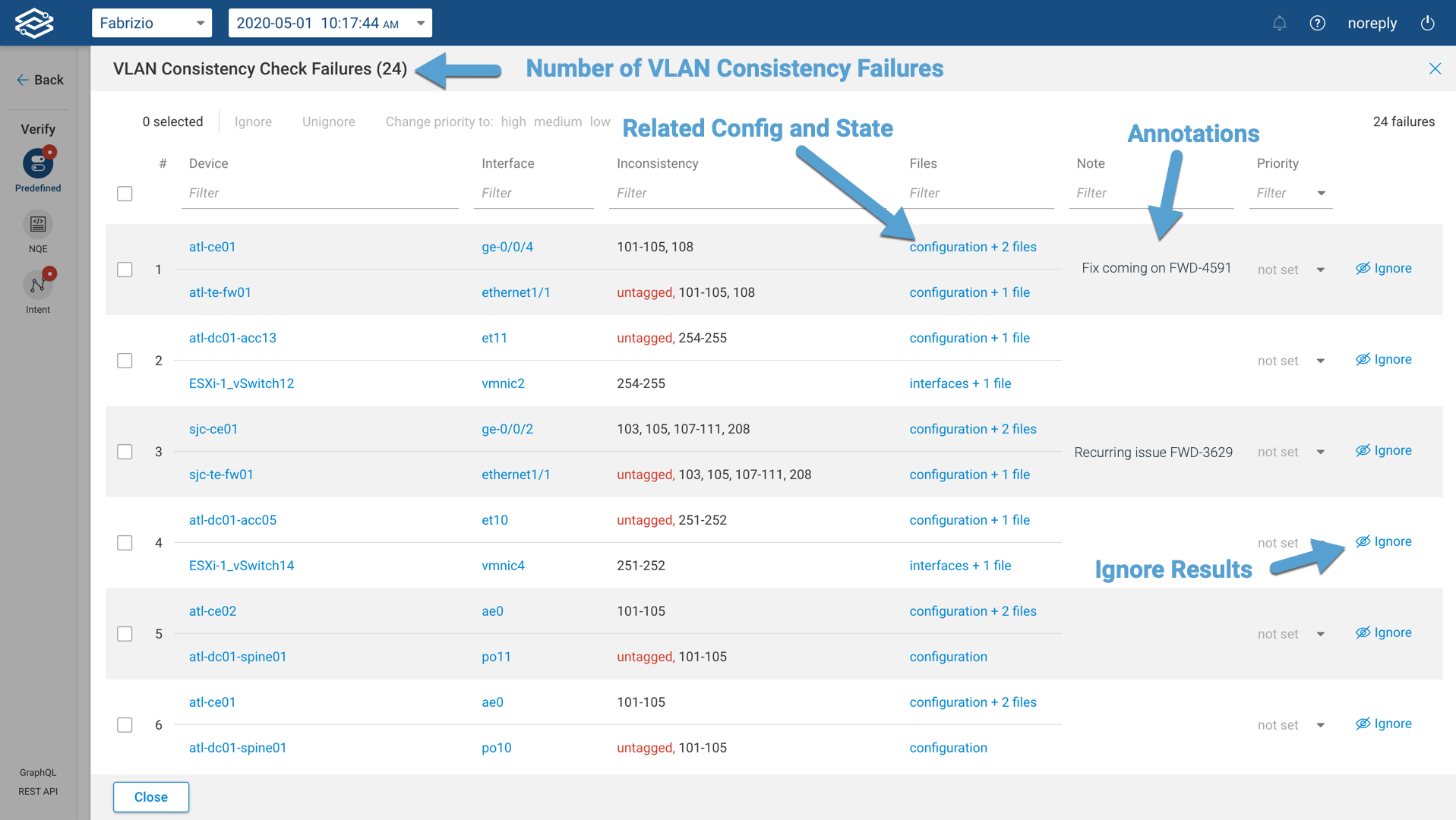
Each result page comes into a table format that can be filtered and sorted. A priority field (high, medium and low) can be assigned to each result, and the user will also be able to add an annotation. Additionally, the user can decide to ignore (hide) a result if deemed not to be important. The goal is to simplify, focus, and accelerate the remediation effort.
The image below shows the result page for the VLAN consistency check:
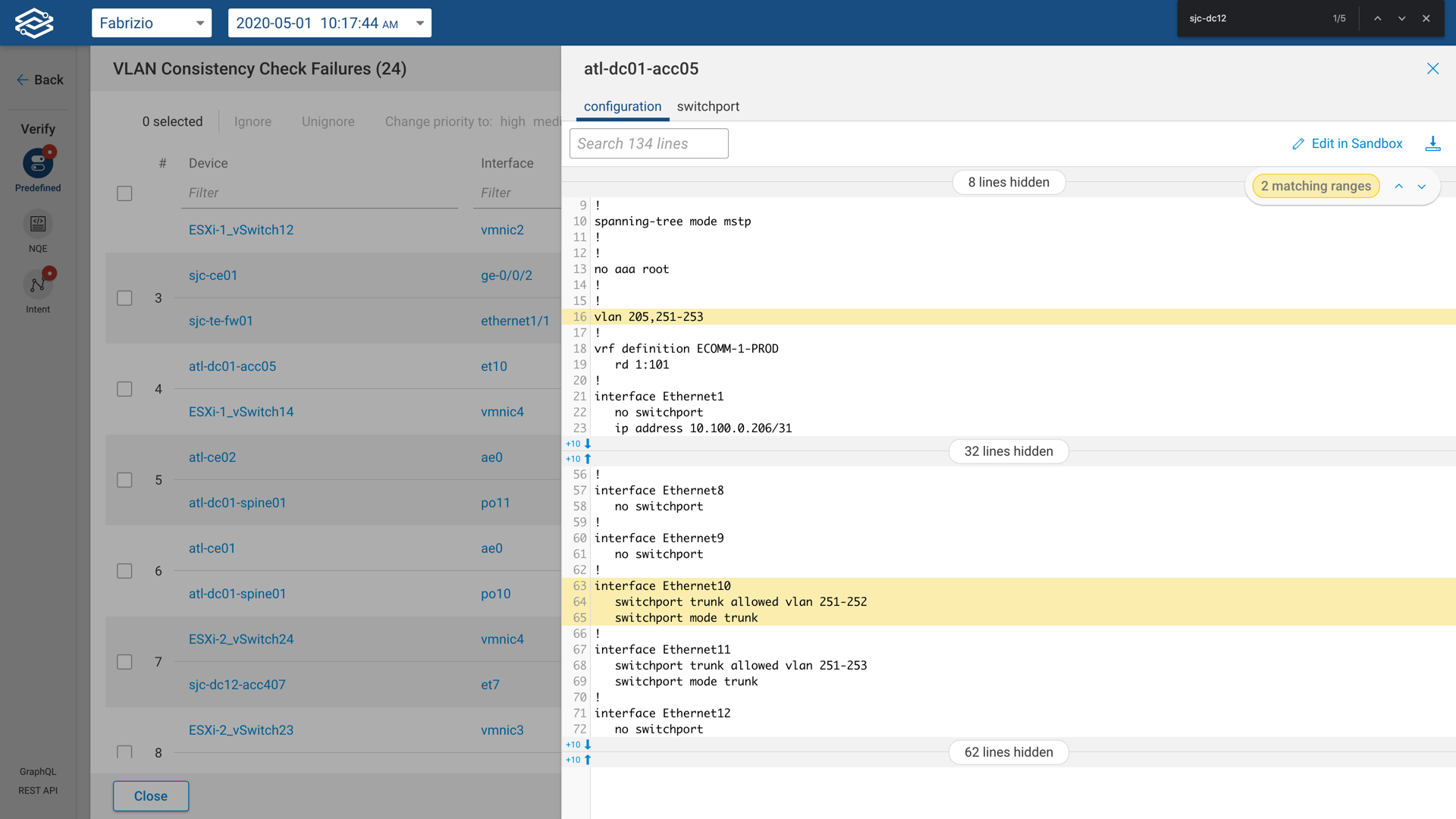
For each individual result, the user can explore the configuration and state responsible for the failure. The system highlights the portion of the file for ease of debugging.
Exporting the Results for Remediation
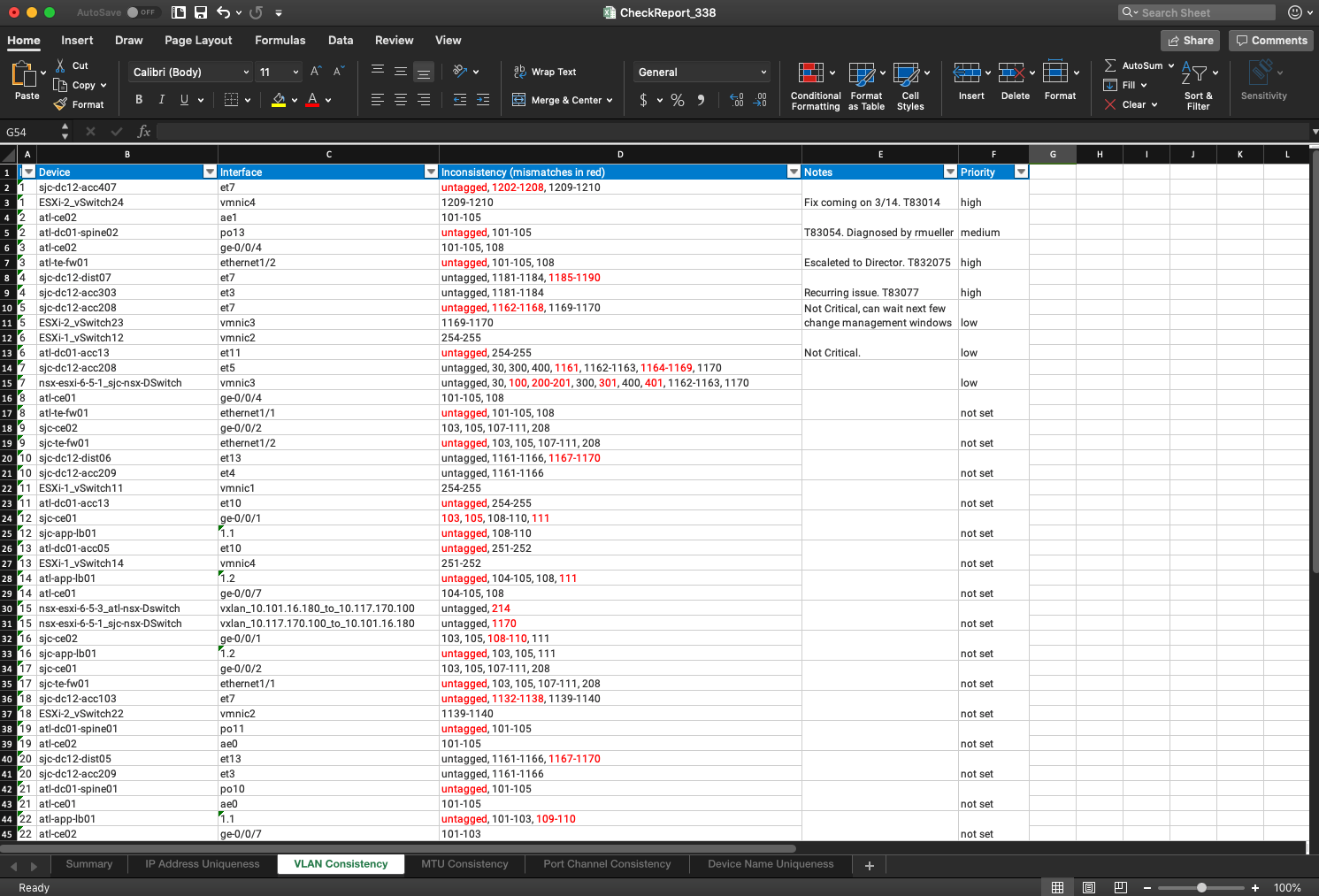
The remediation for the issues found by Forward's Predefined Verification Checks takes place outside the platform. The user can download an Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that contains a tab for each check and its details.
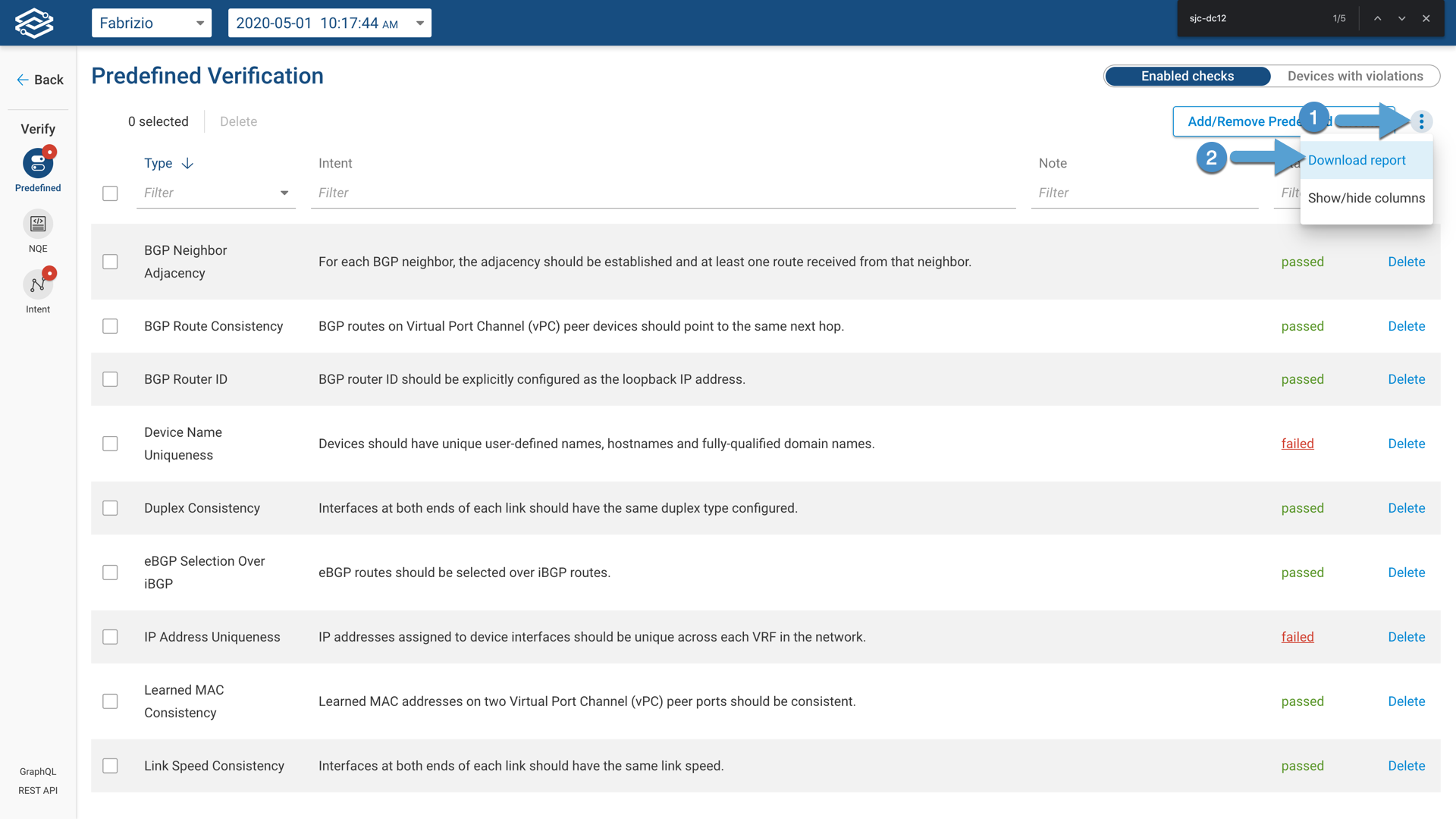
The Microsoft Excel report looks like this: