Install on VMware Hypervisor
Forward Enterprise OVA is compatible with VMware ESXi, 6.5.0 or higher.
Brief System Overview
Forward Enterprise can be installed on one or more nodes (in this document node refers to a VM). The customer can decide to start deploying on a single node and later seamlessly extend the cluster over multiple nodes.
The first installed node is always a primary node. Additional nodes can be installed either as primary or worker nodes. The control plane of the cluster runs on the primary nodes. On multi-node installations, we recommend having 3 primary nodes and adding additional nodes as workers.
A multi-node deployment provides additional value and flexibility:
- Scale-out - When the cluster spans 3 or more nodes, processing is faster and able to use multiple executors. Similarly, search throughput scales with each added node.
- High Availability (HA) - When a cluster is installed with 3 primary nodes, both system and application services are configured to automatically handle node-level failures. As long as no more than a single node goes down at a time, the complete Forward application should remain available, and should not require any administrator involvement (although there may be a transient loss of availability between when the node failure is detected and when application components are restored on other healthy nodes).
- Flexible Resource Allocation - Users can configure resources when using multiple nodes to maximize network scale, minimize the snapshot processing time, or fully isolate different tasks, like processing, search, and collection.
Resource Requirements
Depending on the size and complexity of the networks to be modeled by the platform, we provide different recommendations on number of cluster nodes and hardware requirements of each of those nodes:
| Minimum | Recommended | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Elements | Number of Nodes | Node vCPU | Node RAM | Disk Size* | Number of Nodes | Node vCPU | Node RAM | Disk Size* |
| 1k | 1 | 16 | 128 GB | 150 GB | 1 | 32 | 256 GB | 400 GB |
| 5k | 3 | 32 | 128 GB | 300 GB | 3 or more | 64 | 256 GB | 600 GB |
| 15k | 3** | 32 | 256 GB | 400 GB | 5 or more | 64 | 512 GB | 800 GB |
| 45k+ | 5** | 32 | 256 GB | 1 TB | 7 or more | 64 | 512 GB | 2 TB |
- * Minimum of 3000 write IOPs is required. Minimum of 128MB/s throughput is recommended. NVMe SSD is highly recommended.
- ** Isolated Mode is recommended to ensure full node memory is available for each worker.
Larger networks require more memory to be able to model them. Total vCPUs (across nodes) determine processing speed and search throughput. At least 3 nodes are required for HA support.
Connectivity Requirements
External and Intra-node Connectivity
Each Forward Cluster deployment requires cluster-incoming, cluster-outgoing, cluster-internal, and node-internal connectivity.
It is simpler to allow unrestricted connectivity between cluster nodes. If unrestricted connectivity is not an option, the list of specific ports is noted below. The list below assumes any cluster node can be a primary or a worker node. For additional details about each port and its usage, please contact your Forward Networks representative.
| Source IP | Destination IP | Layer 4 Destination Port |
|---|---|---|
| External | Cluster node | 22 (ssh) |
| Cluster node | Cluster node | 22 (ssh) |
Connectivity to Network Infrastructure
Connectivity from the Forward cluster to network devices or external services is required for snapshot collection, DNS lookups, access to SMTP server, etc. The list of specific ports is noted below. For additional details about each port and its usage, please contact your Forward Network representative.
| Source IP | Destination IP / Address | Layer 4 Destination Port |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster node | Local DNS server | 53 (UDP) |
| Cluster node | Network devices | 22 |
| Cluster node | Cloud Collection: | 443 |
| Cluster node | VMware vCenter | 443 |
| Cluster node | Openflow devices | 6653 |
| Cluster node | SMTP server | SMTP configurable port (if enabled) |
Hostname and IP Address Requirements
Hostnames and IP addresses of cluster nodes should not change. IP addresses must be consistent across reboots, either via static allocation, or persistent allocation with a DHCP server.
Procure the Installation Image
Forward cluster images can be downloaded from Forward Software Central.
Make sure to also obtain the Forward License required to run Forward Enterprise post installation. The license is needed to collect and model the network infrastructure.
The Forward Cluster image is a .ova file which consists of two components:
Forward Enterprise Base: The base component is a stripped-down and hardened Linux image that has been optimized to run the Forward Enterprise application. The Base component also contains the required packages and dependencies to run the cluster orchestration software. The Base component is built using Oracle Linux 8.5 and is updated infrequently.
Forward Enterprise Application: This component contains the Forward Application. Major releases of the Forward Application are published monthly and typically there are several minor releases in each month for bug fixes.
The file name is in the following format forward-base-{BASE_VERSION}-app-{APP_VERSION}.ova, where
BASE_VERSIONhasvN-bMformat (e.g.v9-b4) wherevNshows the major version andbMshows the build number in that version.APP_VERSIONhasyy.m.x-bbformat (e.g.22.8.1-03)yyare the last two digits of the yearmis the month in which the major release was builtxis the minor release number (0 indicates the major release)bbis the build number
Provisioning VMs
Provison one or more VMs in your VMware Hypervisor depending on the desired number of nodes. Nodes should be provisioned using the .ova file downloaded in the previous step.
- Make sure to increase the hard disk's space beyond the provided default and as suggested in the requirement page.
- Also make sure to set the desired number of processor cores.
Example: Deploying a VM on vCenter using vSphere Client
Below instructions and screenshots are taken on vSphere Client version 7.0.2 and steps could vary depending on the vsphere version
-
Login to vCenter using any browser
-
Right-click on the
cluster/resource pooland selectDeploy OVF Template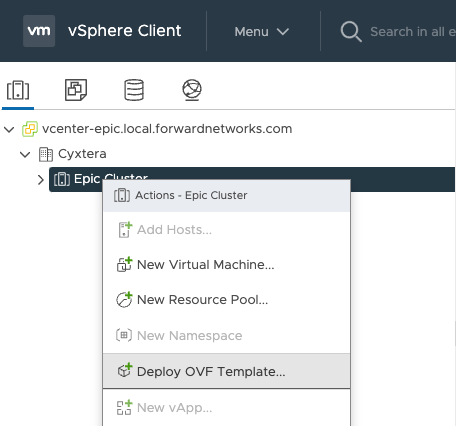
-
Select
Local filesand click onUPLOAD FILESamd select the OVA downloaded previously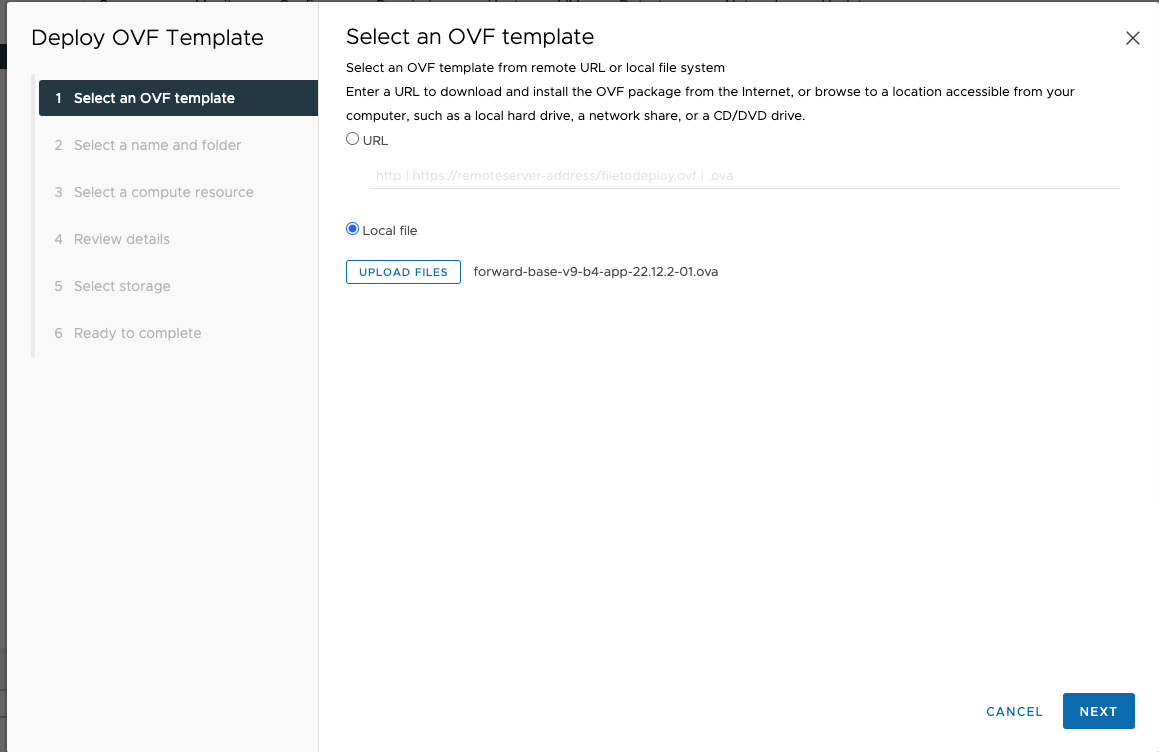
-
Enter the VM name and select the folder to deploy the VM and click
NEXT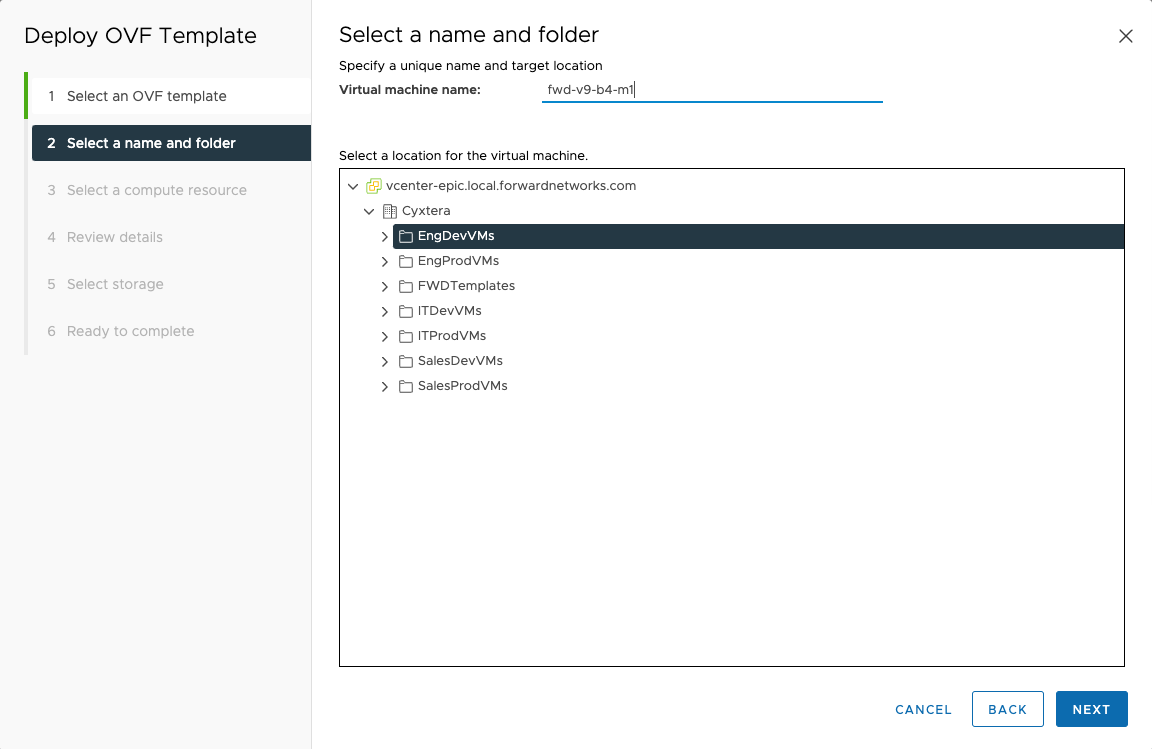
-
Select the resource pool to deploy the VM and click
NEXT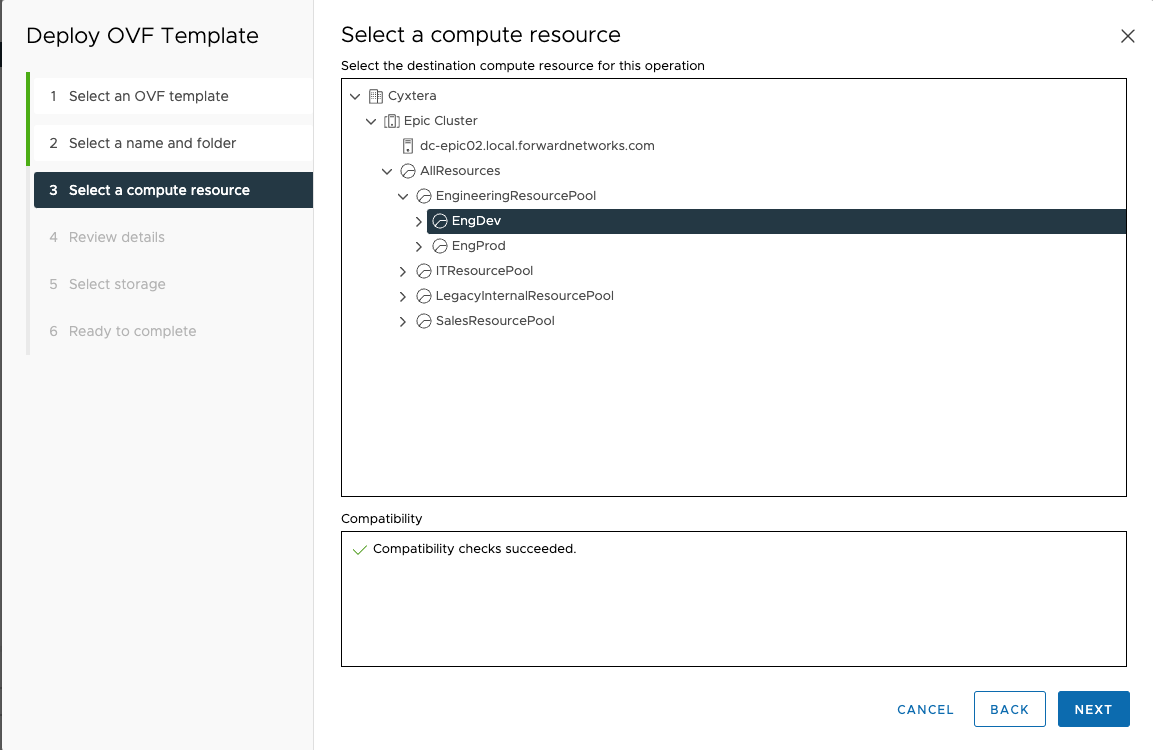
-
Review the details and click
NEXT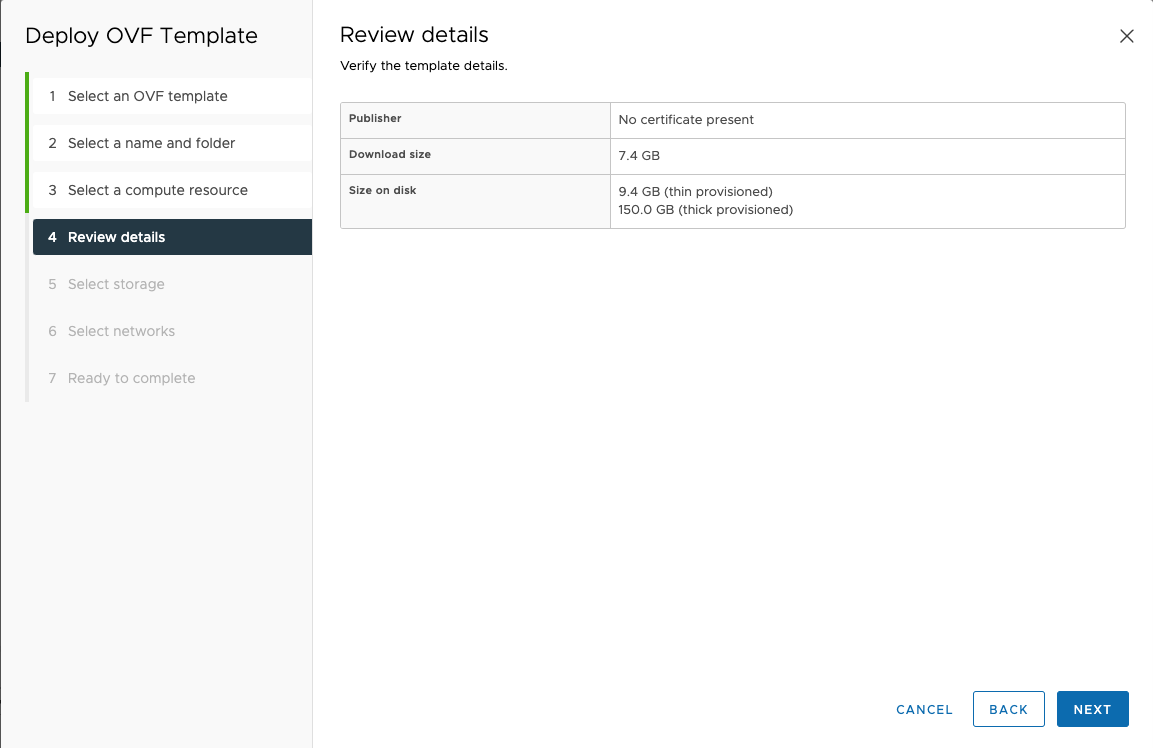
-
Select the datastore which will be used to provision the storage for the VM and click
NEXT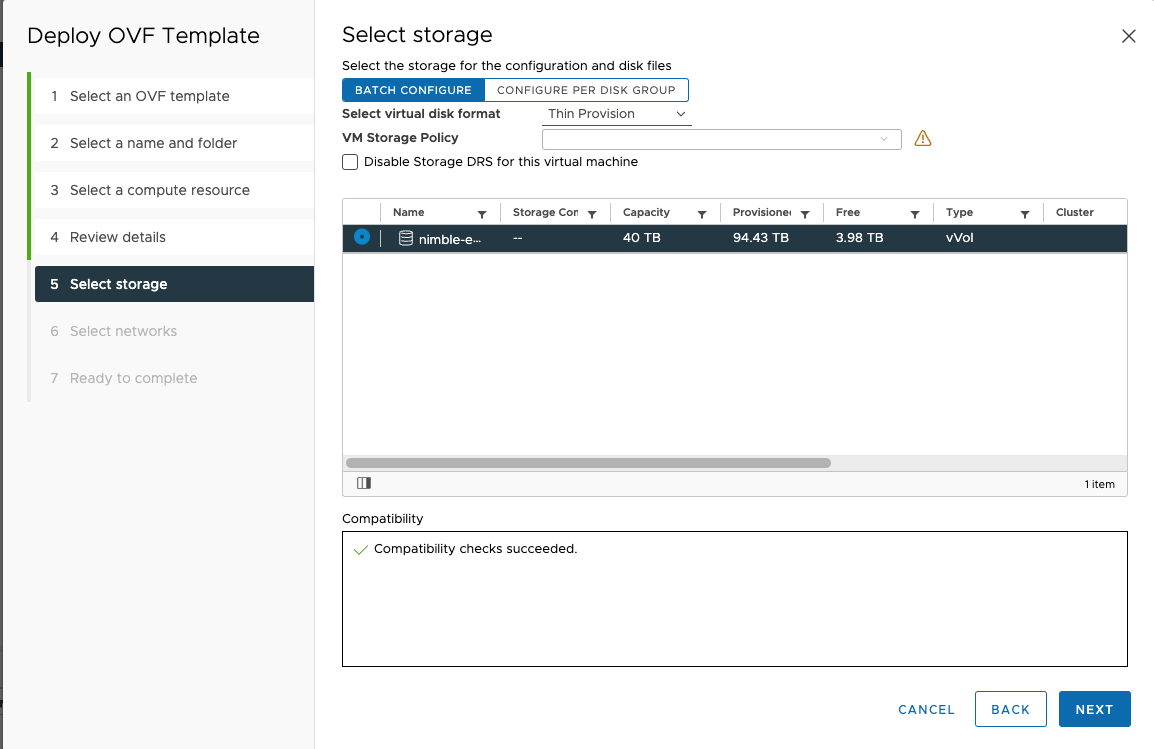
-
Select the Network and click
NEXT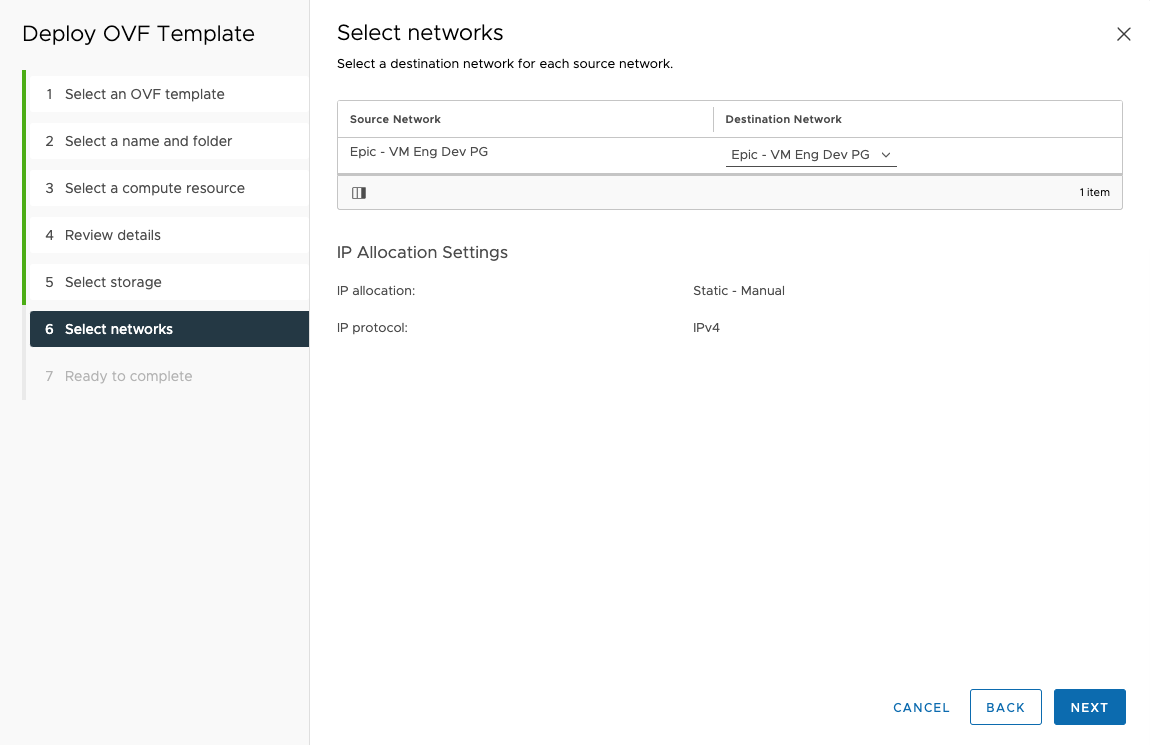
-
Review all the details and click
FINISH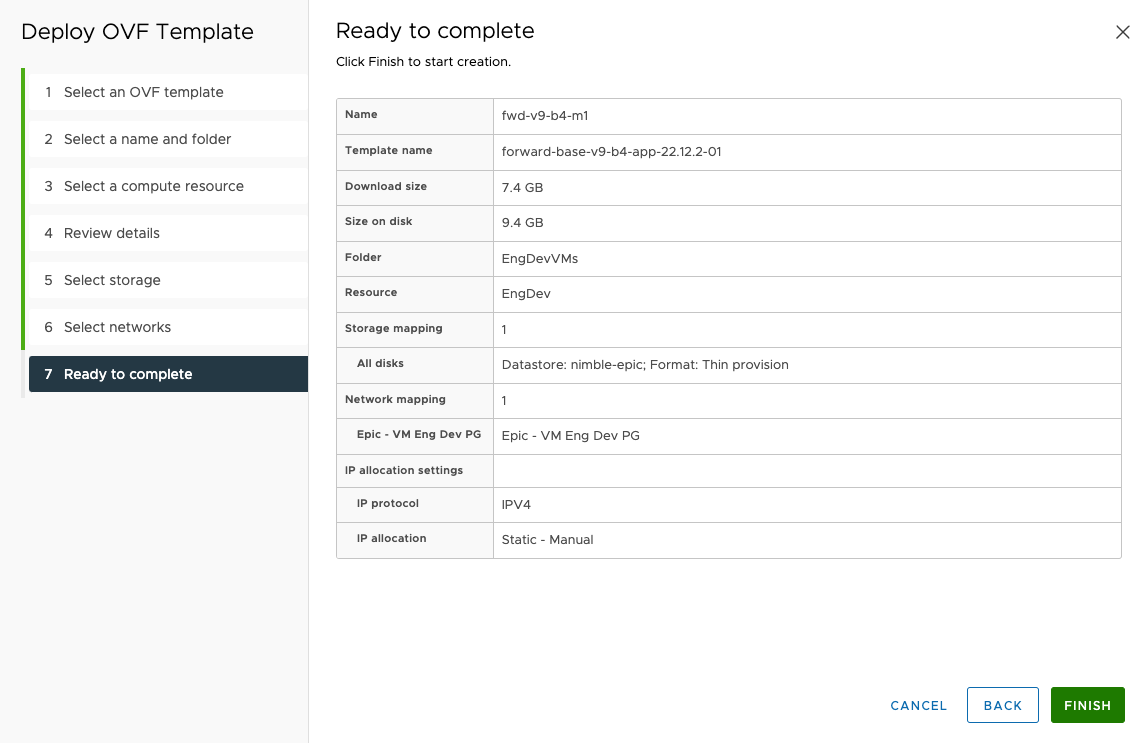
-
Once the VM is deployed click on
ACTIONdropdown and selectEdit Settings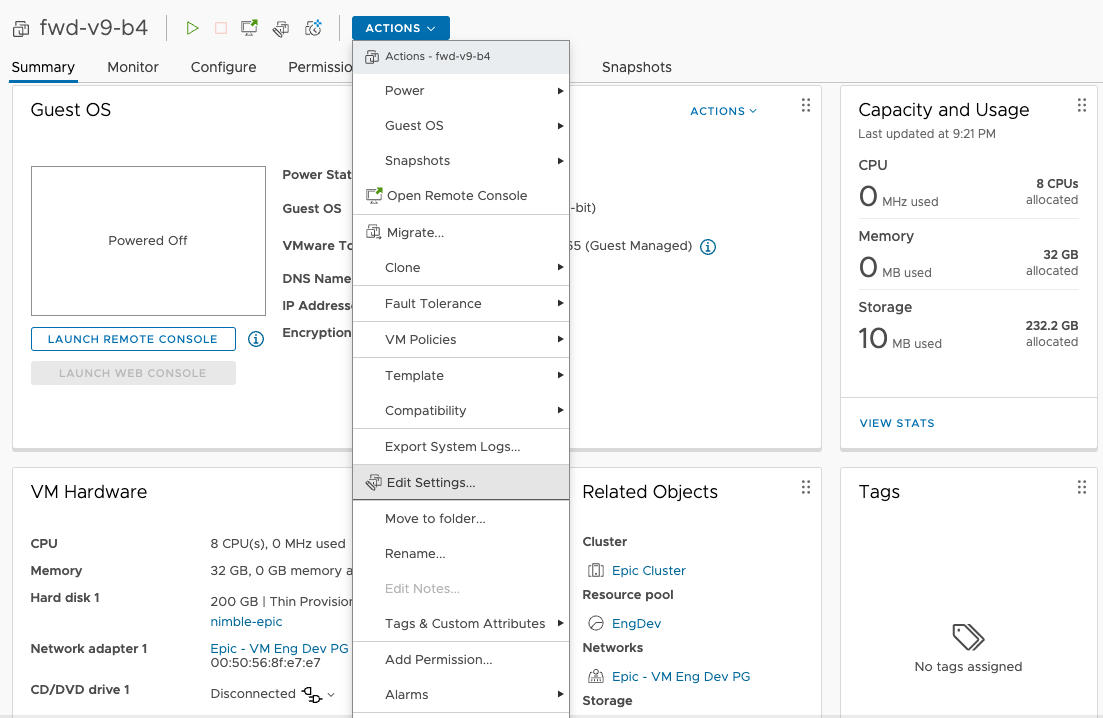
-
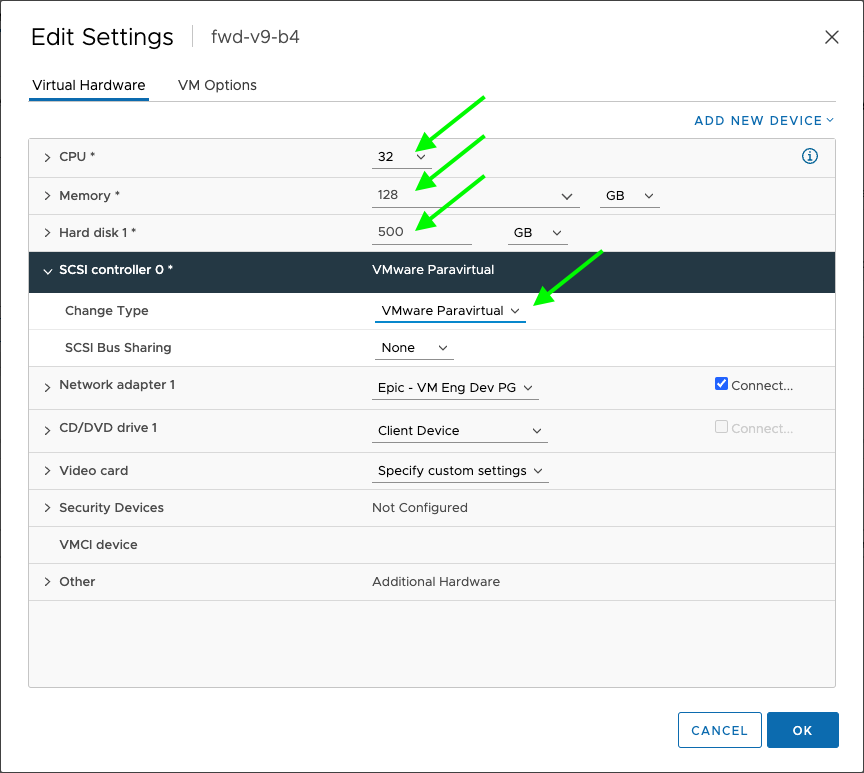
Update the values of CPU, memory and hard disk as per the resource requirements and click
OK[Optional] Enable VMware Paravirtualization which may improve storage performance.
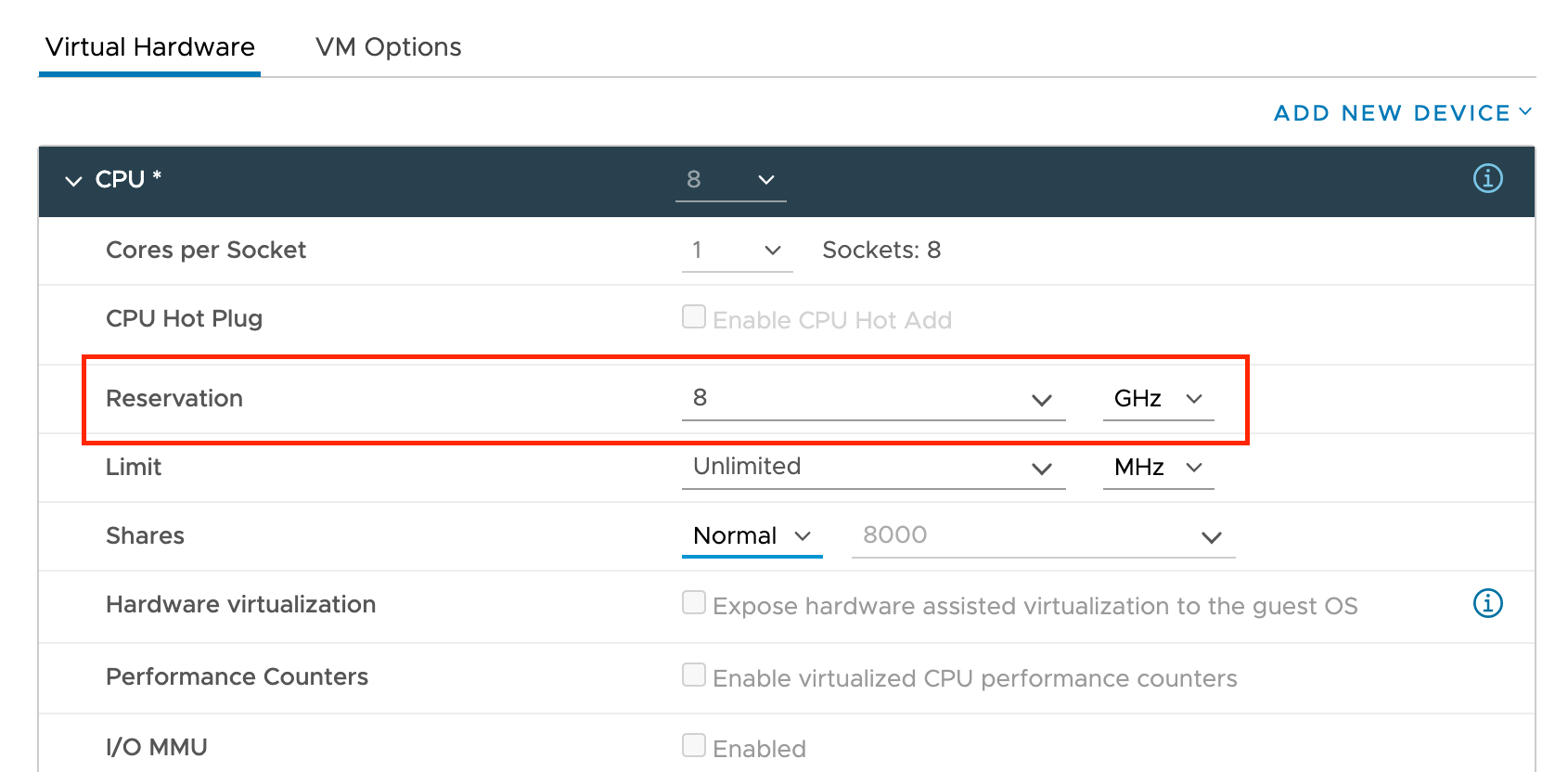
[Optional] Assigning CPU requests to the VM, and setting the reservation at 1GHz per core, are both recommended.
-
Start the VM by clicking on the
ACTIONdropdown and selectPower -> Power On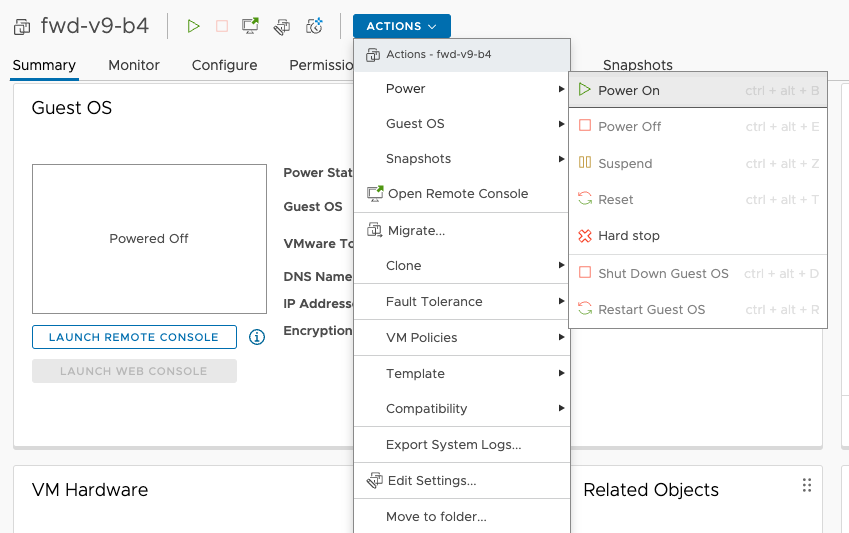
Installation
Log in to a VM that will be one of the primary nodes via SSH, using these default credentials:
- Username:
forward - Password:
changeme
Change the password or add an SSH key and disable password-based logins.
Base Installation
Two subnets are needed for operating the cluster. The fwd-cluster utility will attempt to default to 100.70.0.0/21 and
100.64.0.0/21. If you want to manually pick the subnets to be used, ensure that the pod/service CIDR range is larger
than or equal to /22, as each node in the cluster requires a /24 subnet. This ensures sufficient IP addresses for the
pods running on each node, run the following commands to configure pod/service CIDR after running the fwd-cluster
utility, for example:
fwd-cluster
Forward Cluster> set pod CIDR 10.27.0.0/16
Forward Cluster> set service CIDR 10.16.0.0/16
Where 10.27.0.0/16 and 10.16.0.0/16 are respectively the pod subnet and the service subnet.
Recommended node types based on the cluster size
Note that 2 node clusters are not supported. The number of primary nodes in a multi node cluster must be equal to 3 to ensure high availability.
| Total Number of Nodes in the Cluster | Primaries | Workers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 (not supported) | -- | -- |
| 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 | 2 |
| n (6 or more) | 3 | n-3 |
Steps for provisioning a single-node cluster:
-
Launch the
fwd-clusterutility and follow the steps shown below, to create a single-node cluster (installation takes a few minutes):fwd-cluster
Forward Cluster> add <node_ip> primary [hostname]
Forward Cluster> applyEnsure that the
hostnameprovided is unique -
The installation was successfull if you see this message at the end:
Base installation is complete. -
You may now exit the
fwd-clusterutility using theexitcommand.
Steps for provisioning a multi-node cluster:
For a multi-node cluster the steps for creating a primary node are the same as single-node cluster. We can follow the same steps to add additional primary and worker nodes as shown below.
-
To add a primary node to the cluster, please launch the
fwd-clusterutility and run the commandaddas shown below:fwd-cluster
Forward Cluster> add <node_ip> primary [hostname]Ensure that the
hostnameprovided is unique. In addition, it is important to ensure that number of primaries added adhere to the recommendations in the table mentioned above -
To add a worker node, please run the following steps:
Forward Cluster> add <node_ip> worker [hostname]Ensure that the
hostnameprovided is unique -
[Optional] At any given point, you may verify the list of nodes added by running the command
list:Forward Cluster> list -
Once the desired number of nodes are added, provision the cluster by running the command
apply:Forward Cluster> apply -
The installation was successfull if you see this message at the end.
Base installation is complete. -
You can now exit the
fwd-clusterutility using theexitcommand.
App Installation
Install Forward application using the commands shown below using the fwd-cluster utility.
Forward Cluster> app install [included | path to forward-app-yy.mm.x-bb.package]
Running the command app install included installs default package that comes with the base.
Running the command app install alone will trigger a prompt asking whether to install the default app version. You may
type "yes" and press ENTER to install the default package that comes with the base or "no" to provide the path to the
desired forward-app-yy.mm.x-bb.package.
Running the command app install (path to forward-app-yy.mm.x-bb.package) will install forward package provided at the
path.
Browser Access
Before accessing the application with a web browser, please note the following:
Upon the first login, the system will ask to change the password. Be ready to store it in a safe place. The user will be able to configure external authentication mechanisms like LDAP, SSO and TACACS after the first login.
It is now time to access the browser and log into the Forward UI using the following default credentials (the system will ask to change the password):
- username:
admin - password:
forward
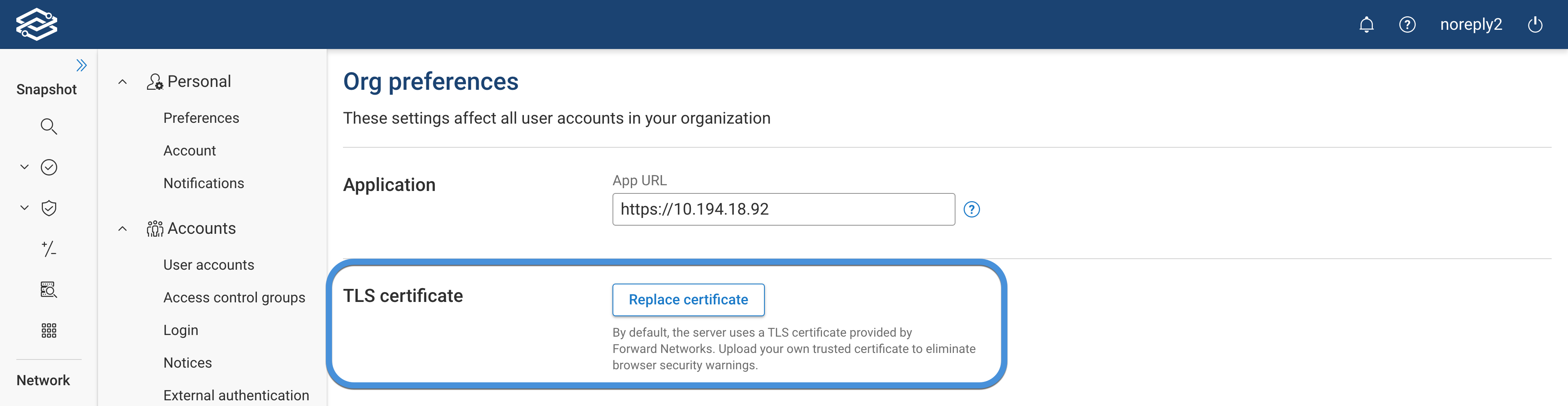
Set the TLS certificate
By default, the server uses a TLS certificate provided by Forward Networks.
Upload your own trusted certificate in the Settings --> System -->Org Preferences page to eliminate browser security warnings.
The server will be restarted after the certificate is uploaded, and may be unavailable for up to 5 minutes.
Optional: Set up load balancing
If you have installed 3 primary nodes, the control plane of the cluster is already running in HA mode. Assuming the IP address of these nodes are primary1-ip, primary2-ip and primary3-ip, you can reach the application through any of the following addresses:
https://primary1-ip/
https://primary2-ip/
https://primary3-ip/
However, if users use one of these addresses and that node is down, they will see failures. To have proper HA, it is better to use a load balancing option which has health checks. To do that you need a reverse proxy which forwards requests to port 443 to any of the healthy nodes in the cluster.
The following methods can be used to perform health checks:
- TCP health checks on port
443. - HTTP health checks that issue
GET /pingand expect 200 status code.
Sample configuration for HAProxy with http checks
# Frontend that accepts requests from clients
frontend fwd-app
bind *:443
# Mode is the mode the frontend is operating (TCP or HTTP)
mode tcp
# Enable advanced logging of TCP connections with session state and timers
option tcplog
# Maximum inactivity time on the client side
timeout client 9000s
default_backend fwd-app
# Backend servers that fulfill the client requests
backend fwd-app
# Enable HTTP protocol to check on the servers health
option httpchk GET /ping
# HTTP health checks to validate the response status code to be 200
http-check expect status 200
# Use SSLv3 client hello health checks for server testing
option ssl-hello-chk
# Use roundrobin load balancing algorithm
balance roundrobin
# inter : Time interval between two consecutive health checks
# downinter : Time interval between two consecutive unhealthy checks
# rise : server will be considered as operational after <count> consecutive successful health checks
# fall : server will be considered as dead after <count> consecutive unsuccessful health checks
# slowstart : time after how long a server which has just come back up will run at full speed
# maxconn : Maximum number of concurrent connections that will be sent to this server
# maxqueue : Maximum number of connections which will wait in the queue for this server
# weight : used to adjust the server's weight relative to other servers
default-server inter 10s downinter 5s rise 2 fall 2 slowstart 60s maxconn 250 maxqueue 256 weight 100
server server1 <primary1-ip>:443 check
server server2 <primary2-ip>:443 check
server server3 <primary3-ip>:443 check
Sample configuration for HAProxy with tcp checks
frontend fwd-app
bind *:443
mode tcp
option tcplog
timeout client 9000s
default_backend fwd-app
backend fwd-app
mode tcp
option tcplog
# Perform health checks using tcp-check send/expect sequences
option tcp-check
timeout server 9000s
balance roundrobin
default-server inter 10s downinter 5s rise 2 fall 2 slowstart 60s maxconn 250 maxqueue 256 weight 100
server server1 <primary1-ip>:443 check
server server2 <primary2-ip>:443 check
server server3 <primary3-ip>:443 check
Sample configuration for F5 load balancer
# create monitor (HTTPS request for "GET /ping" from server, if code 200 => server is up)
tmsh create ltm monitor https fwd_https { send "GET /ping \r\n" recv "^HTTP.1\.[0|1]\s+200" }
# create pool of servers with monitoring
tmsh create ltm pool FwdPool members add { <primary1-ip>:443 <primary2-ip>:443 <primary3-ip>:443 } monitor fwd_https
# create virtual server for load balancing (ip <ip address>), works only for TCP 443 traffic, balanced to all living
servers in pool
tmsh create ltm virtual FWDvServer { destination <ip address>:443 mask 255.255.255.255 pool FwdPool ip-protocol tcp translate-address enabled }
Configure License
Please follow the instructions here for configuring the license.